New Product Development Tool
The benefits of a formal NPD process are:
- Puts discipline into an ad hoc and chaotic process
- Provides a roadmap for the project leader, defining his/her tasks and deliverables
- It is a visible process known and understood by everyone in the company
- Forces more attention to quality of execution. The evaluation points are the quality control checkpoints.
- Creates a complete process – there are no missing steps
- It is multi-functional – it forces input from all parties
- It is faster – activities are done concurrently rather than sequentially
Download Project Management Tools
This NPD framework provides go/kill decisions at five gates, at each of which a project must apply for further funding. At the first gate an idea seeks funding for an initial few days of work, and has to meet only the simple criteria that it appears to be technically feasible, it appears to have market feasibility, and it is in line with company strategy. Other phases and gates in the process are designed to:
- Manage and support the process for generating, collecting and reviewing new ideas or concepts.
- Estimate the wealth creation potential of each idea and continuously review it if the idea is taken forward.
- Ensure that during the implementation phase the minimum time to final commercialisation is achieved.
- Tear down the walls that separate research, design, and manufacturing.
- Set the criteria for passing from one phase to another - which is set out in advance. Decision makers include representatives of all company functions.
- Use manufacturing as a respected place where the value of the idea is realised.
- Deliver innovative new products quickly and at competitive price. This requires an efficient and effective supply chain.
An important function of gate committees is to check that not only has the required work been done, but that it has been done with sufficient quality.
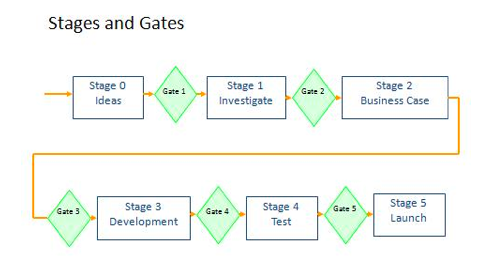
| Stage 0 | Generating ideas |
Encourage everyone to take
an active part in offering new ideas. Make a rough estimate of market
attractiveness and technical feasibility, state how benefits to customers
exceed those of competitors |
| Gate 1 | Initial screen | If the idea looks feasible, and it fits with the organisation’s strategy, authorise investigation with allocated resources up to £5k. |
| Stage 1 | Preliminary investigation | One week of desk research, some concept testing on customers, market growth / competition estimates, using a small team from marketing & development. |
| Gate 2 | Second screen | More critical review of the results of stage 1. Go / Kill / Hold decision. Agree a budget for stage 2. |
| Stage 2 | Build business case | Detailed investigation of attractiveness and profits, involve more cross-functional full time core team members: a) user needs-and-wants studies, b) economic benefits, c) swot-analysis on global competitors, d) uniqueness of product e) concept testing, f) technical and legal feasibility, g) manufacturing, investment and training costs, h) detailed financial analysis, i) clear definition of product/ price/ placing / promotion, j) full details of business model and value chain. |
| Gate 3 | Decision on business case | Review of stage 2. Go / Kill / Hold decision. Approve the project as a core programme. Allocate budget for full-scale development. |
| Stage 3 | Development | Lab testing, prototyping, formalised customer tests, a) agreement between marketing and manufacturing involving the voice of the customer, b) detailed plans for test, full scale market launch, production (facilities), c) updated financial analysis, d) regulatory, legal, patent issues resolved. |
| Gate 4 | Pre-manufacturing review |
Review of stage 3. Freeze the specification. Allocate manufacturing resources. |
| Stage 4 | Manufacturing implementation | Testing in true environment, a) extended lab tests of quality and performance, b) trial / limited / pilot production - proved and debugged, c) field trial use in small groups of customers, test market / trial sell in limited territory, measure effectiveness of launch plan, d) re-estimate financial returns, e) life cycle plan for long term revision / out phasing of the product. |
| Gate 5 | Final decision point | Review of stage 4. Approval of launch and life cycle plans. Full commercialisation. Commitment to delivery dates. |
| Stage 5 | Full production and market launch | Realisation stage. On-going after-sales service. Monitoring of processes and suppliers. |
| Gate 6 | Post-implementation | 12 months after launch, revised financial performance analysis, the finishing point of the project. Post-market surveillance. |

Stay Connected